Glossary - alphabet order - "C"
CD
This is the symbol for drain capacitance. See "crystal oscillation circuit".
Reference: Crystal oscillation circuit
CG
This is the symbol for gate capacitance. See "crystal oscillation circuit".
Reference: Crystal oscillation circuit
CI
Abbreviation for "Crystal Impedance". See "equivalent series resistance".
Reference: Equivalent circuit of crystal unit
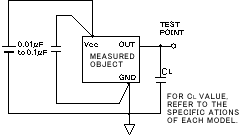
CL
This is the symbol for load capacitance. See "load capacitance".
Reference: Load capacitance
CMOS
Abbreviation for "Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor", which is a type of LSI structure. This is the main type of LSI used today.
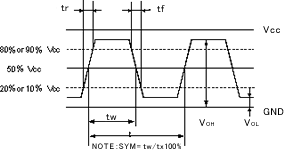
CMOS load
This refers to a circuit that includes a CMOS structure (a type of IC structure) and that has a load circuit connected to the output. The high/low threshold is 50% Vcc.
 |
 |
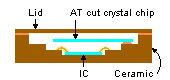
Ceramic package
A ceramic package uses ceramic as part of its package material. To maintain the characteristics of a crystal device over a long period of time, the container must be hermetically sealed. This is why metal materials have been used in the past for packages. Today, ceramic materials are used for compact SMD products.
 |
 |
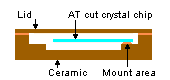 |
| Example of ceramic package product | Structure of ceramic package product | |
Clock Oscillator
A clock oscillator is a type of crystal oscillator that provides the square wave pulse required by computers and other digital equipment. Although a clock oscillator has the same configuration as a crystal oscillator that generates accurate frequencies, it is used for different applications. Epson offers clock oscillators in SG series.
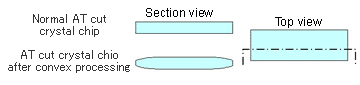
Convex processing
Convex processing creates curved surfaces on both ends of an AT cut crystal chip. To obtain a lower frequency for thickness shear vibration, the chip's thickness must be greater. Larger energy is required to vibrate larger mass.
Rounding out the ends of the crystal chip makes the chip's vibration become concentrated in the middle, which enables efficient oscillation using less energy. This process is employed not only for low-frequency crystal chips but also for compact crystal chips.
Reference: AT crystal unit , Thickness shear vibration
Crystal filter
A crystal filter is a crystal device that is used to pass through and or cut off frequency range within a frequency band. The crystal filter has superior temperature characteristics when compared to filters that use other materials. Currently, the crystal filters cover up to about 100 MHz, and SAW filters are used at any higher frequency band.
Reference: SAW filter
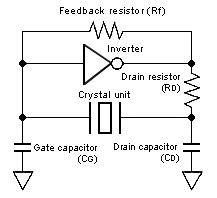
Crystal oscillation circuit
A crystal oscillation circuit is used to drive a crystal unit. The drawing at right shows a crystal oscillation circuit typically used with CMOS ICs.
Reference: Oscillation circuit parameter
Crystal oscillator
A crystal oscillator is a crystal device that is able to output a specified frequency because a crystal oscillator and a crystal oscillation circuit (IC) are incorporated into a single package. A stable frequency can be obtained because matching adjustments between the crystal unit and crystal oscillation circuit has been completed. Epson recommends using crystal oscillators rather than crystal units.
 |
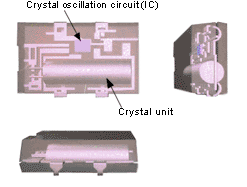 |
| External view (left) and perspective view (right) of plastic package's crystal oscillator |
|
 |
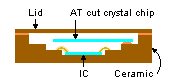 |
| External view (left) and structural drawing (right) of ceramic package's crystal oscillator |
|
Crystal unit
This is a crystal device that a crystal chip is enclosed in a package. Crystal units can be classified into tuning fork crystal units, AT crystal units, or SAW resonators, depending on the type of crystal chip used.
Reference: Tuning fork crystal unit , AT crystal unit , SAW resonator
