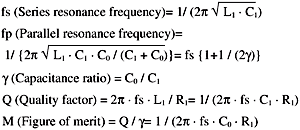about Crystal unit/General
1. Vibration Modes and Orientation Angles
2. Frequency- temperature characteristics
3. Equivalent circuit and various constants
General
1. Vibration Modes and Orientation Angles
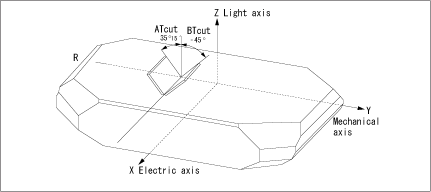
Regarding the vibration mode of the AT cut, the orientation angle at which the primary coefficient of the frequency temperature characteristics near room temperature reaches zero is indicated in Fig.1
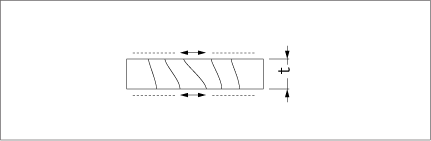
And the mode of thickness shear vibration is shown virtually in Fig.2
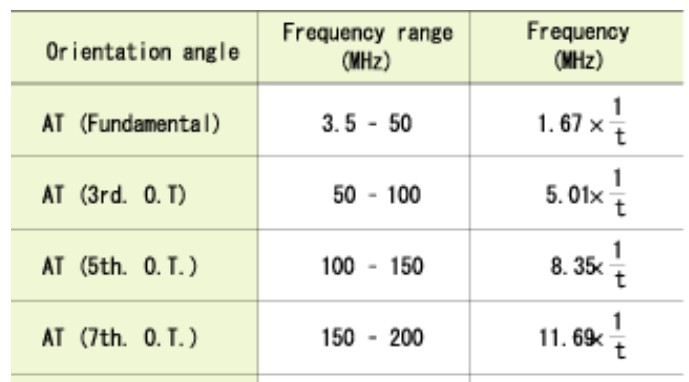
Regarding generally used AT cut crystals, their frequency ranges and frequency coefficients (the relationship between the thickness of crystal plate and oscillation frequency) are shown in Table 1.
2. Frequency-temperature characteristics
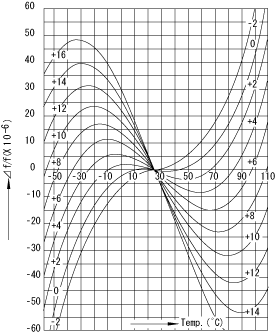
The frequency-temperature characteristics of a crystal are categorized into two types according to its shape of curve. One is a tertiary curve and the other is a quadratic curve. The typical frequency-temperature characteristics of AT cut are shown in Fig.3 and Fig.4, respectively. AT cut crystal units are most widely used because they produce smaller frequency changes in response to temperature changes in the room temperature range.
3. Equivalent circuit and various constants
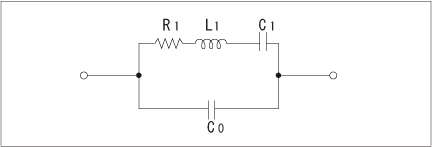
The equivalent circuit of quartz crystal near the resonance frequency is represented by the arrangements shown in Fig.5.
R1:Series Resistance
L1: Motional Inductance
C1: Motional Capacitance
C0: Shunt Capacitance
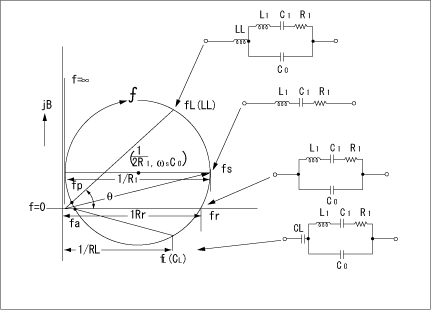
The admittance locus diagram of a crystal unit near its oscillation frequency and the equivalent circuit of a crystal unit are shown in Fig.6.This chart and figure show the configuration of the equivalent circuit under various circuit conditions and the relationship between oscillation frequency and resistance, etc.Here, we can find the following relationships among the various constants